Top
Math 147 - Fall 1997 - Test #1
Name:______________________________________ Section Number:_______________(2 points)
Show ALL your work. Solutions with no work where it is necessary will receive no credit. If in doubt, show everything necessary for the computation. If you need extra paper, use the back of the test or raise your hand and ask a proctor for some. If work is located on the back of a page please indicate this on the front of the page. A normal table is provided at the end of the test.
For 1 - 10 (3 points each) circle the answer which best completes the sentence or answers the question.
- You can compute the standard deviation of a large set of data if you have,
- the maximum, minimum, and average of the entries in the data set.
- all of the entries in the data set.
- the value (entry - average) for each entry in the data set.
- either (a) or (b).
- either (b) or (c)
- A histogram of data with a long right tail indicates the data,
- has a very large positive average.
- has an average smaller than its median.
- has an average larger than its median.
- was obtained in a manner producing bias.
- both (a) and (c).
- A study on height of males at Alfred University revealed an average height of 70 inches with a standard deviation of 2.0 inches. Your friend Bill is 78 inches tall, we can conclude,
- the sampling method of the study was biased.
- less than one percent of males at Alfred University are likely to be taller than Bill.
- Bill is four standard units above the average.
- both (a) and (c).
- both (b) and (c).
- When using the model: individual measurement = exact value + bias + chance error
it is important to remember,
- The bias is assumed to be the same for all measurements.
- The chance error is always smaller than the bias.
- The bias fluctuates from measurement to measurement and its average should be determined.
- The size of the bias can usually be detected by comparing the mean to the median.
- both (a) and (b).
- You have been involved in a large study of intelligence quotients ( IQ scores). When you received your score, it placed you in the 59 th percentile. According to the results of this study you can conclude,
- your IQ score was higher than the average of the study.
- approximately 59% of those taking the test scored lower than you.
- your score was higher than the median of the study.
- both (b) and (c).
- (a), (b), and (c) are all true.
- Consider the following statements:
( I ) If the size of the list of data is large enough then any bias in the measuring process can be ignored.
( II ) Quantitative data is numerically represented.
( III ) If three is added to all the numbers in a list then the standard deviation of the list will
increase by a factor of nine.
( IV ) If ten is added to all the numbers in a list then the average of the list will increase by ten.
What can be said about statements I - IV ?
- statements I, II, and IV are true.
- statements II and IV are true.
- statements II, III, and IV are true.
- all of the above statements are true.
- none of the above statements are true.
- Consider the line: y = 2x - b, where b is some number we do not know.
If you are told that the point (1, 2) is on the line then which of the following points is also on the line.
- (2, 4) (d) (4, 4)
- (1,-3) (e) (b, 3)
- (2, b)
- If we have a normal curve with an average of three and a standard deviation of two then,
- the area under the curve between 1 and 5 is 95.0%.
- the area between 3 and 9 is 49.85%.
- the total area under the curve is 99.7%.
- the area to the left of three is 50.0%.
- both (d) and (b) are true.
- In an observational study,
- confounding factors are easily controlled for.
- a placebo is always used.
- participants are randomly assigned to a control and an experimental group.
- we must always rely on historical controls.
- participants assign themselves to the various groups being studied.
- A researcher makes random phone calls until she contacts 10 smokers and 10 non-smokers for a smoking vs. body weight study. Her study,
- is an observational study.
- has controlled for confounding factors.
- is a randomized controlled experiment.
- makes use of a placebo.
- both (b) and (c).
- Find the area under the normal curve
- (5 points) between z = -0.5 and z = 1.0
(b) (5 points) to the right of 1.5
12. Given the following data set: 6, -1, -3, 0, -2
Compute:
- (3 points) the average of the data.
- (5 points) the standard deviation of the data.
- (2 points) the median of the data.
13. The exam scores for the first Math 147 exam last year were approximately normal with an average of
83 and a standard deviation of 5.
- (6 points) Your roommate was in the class last year and scored an 89, what percentile was she in?
- (8 points) To get into medical school, you need to be in the 95th percentile. What score would you need if this years test is similar to last years test?
- (5 points) Find the percentage of students last year that had exam scores between 80.5 and 88.
14. Below is a histogram (figure 1) of final exam scores for my calculus I class for last semester.
Answer the questions below figure 1. The vertical scale is % per point. ( All the tops of the bars
match up with a number on the vertical scale.)
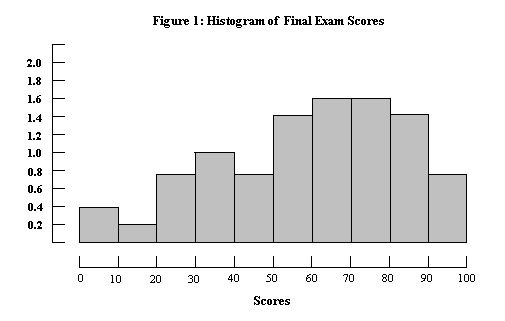
- (5 points) Thirty-two percent of the class scored between 60 and 80. What percent had scores between 0 and 20.
- (5 points) Estimate the 92th percentile of the test scores.
- (5points) About what percentage of students scored between 30 and 60?
- (3 points) The median of the test scores is between what two scores on the horizontal axis?
15. (a) (4 points) Find the equation of the line that passes through the point ( - 1, 2) that has a
slope of 2.
(b) (5 points) Sketch the graph of the line. (Neatness is important)
- (2 points) The point (3,4) is on the above line. Circle one:
True False
| Top | Home | Answer Key |

